
FSolver can not be held responsible for the use made of each of the answers to the questions asked. The answers to the questions asked by users are treated and exploited by them under their own responsibility. The answers proposed to users are processed and exploited by them under their own responsibility. This application is available in 7 languages (French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, German, English and Catalan) and works in the same way in all languages. All information, data, text, tables, photographs, graphics, content on the site - with the exception of content accessible via links - constitute a database for which, under the laws in force, the owner of the site holds property rights.Īrticle 2 : The purpose of the site and its contentsįSolver is an Internet application for personal use that allows you to find solutions to crossword and word puzzle grids. Users view and use the Site on their own behalf. Use of the Site does not constitute a right of ownership of the data made available. Any reproduction, even partial, of the content of FSolver is prohibited without the express written permission of the site owner. However, it should be noted that the definitions come from the excellent website. The site FSolver, the contents and the software which compose it are the property of the owner of the site. Users: any natural or legal person who uses the siteĪrticle 1 : Ownership of the site and the elements that compose it.
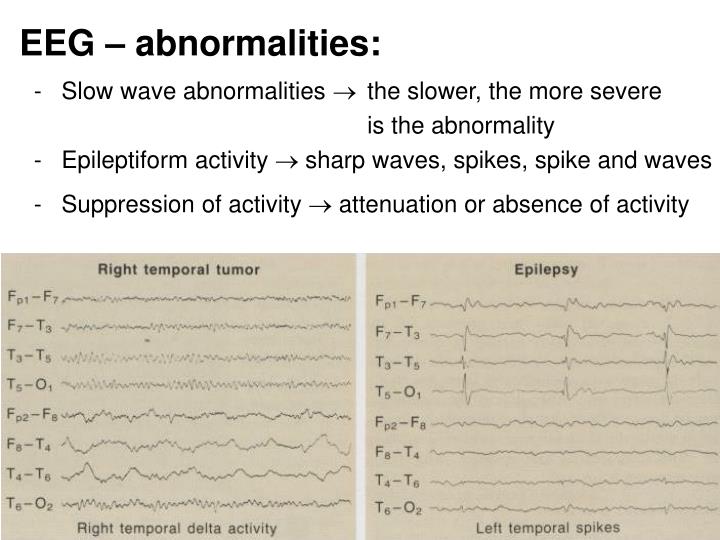
Taking the crown for perhaps the most uninspired name of EEG findings, 14 and 6 positive spikes describe 1-2 second bursts of sharply contoured positive waveforms that come in frequencies of either 14 Hz (13-17 Hz) or 6 Hz (5-7 Hz), or an admixture of both.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
